起步 MYSQL的依赖 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 2.3.0</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-j</artifactId > <scope > runtime</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId > <scope > test</scope > </dependency > </dependencies >
POJO的准备 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class User { private Integer id; private String name; private Short age; private Short gender; private String phone; }
连接准备 application.properties:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 spring.datasource.driver-class-name =com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url =jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis spring.datasource.username =root spring.datasource.password =1234
Mapper层 在创建出来的springboot工程中,在引导类所在包下,在创建一个包 mapper。在mapper包下创建一个接口 UserMapper ,这是一个持久层接口(Mybatis的持久层接口规范一般都叫 XxxMapper)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import com.itheima.pojo.User;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;import java.util.List;@Mapper public interface UserMapper { @Select("select id, name, age, gender, phone from user") public List<User> list () ; }
连接池 概念 没有使用数据库连接池:
客户端执行SQL语句:要先创建一个新的连接对象 ,然后执行SQL语句 ,SQL语句执行后又需要关闭 连接对象从而释放资源,每次执行SQL时都需要创建连接 、销毁链接,这种频繁的重复创建销毁的过程是比较耗费计算机的性能。
数据库连接池是个容器,负责分配、管理数据库连接(Connection)
程序在启动时,会在数据库连接池(容器)中,创建一定数量的Connection对象
允许应用程序重复使用一个现有的数据库连接,而不是再重新建立一个
客户端在执行SQL时,先从连接池中获取一个Connection对象,然后在执行SQL语句,SQL语句执行完之后,释放Connection时就会把Connection对象归还给连接池(Connection对象可以复用)
释放空闲时间超过最大空闲时间的连接 ,来避免因为没有释放连接而引起的数据库连接遗漏
引入与实践 官方(sun)提供了数据库连接池标准(javax.sql.DataSource接口)
如果我们想把默认的数据库连接池切换为Druid数据库连接池,只需要完成以下两步操作即可:
参考官方地址:https://github.com/alibaba/druid/tree/master/druid-spring-boot-starter
在pom.xml文件中引入依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba</groupId > <artifactId > druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 1.2.8</version > </dependency >
在application.properties中引入数据库连接配置
方式1:
1 2 3 4 spring.datasource.druid.driver-class-name =com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.druid.url =jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis spring.datasource.druid.username =root spring.datasource.druid.password =1234
方式2:
1 2 3 4 spring.datasource.driver-class-name =com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url =jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis spring.datasource.username =root spring.datasource.password =1234
Lombok 介绍 Lombok是一个实用的Java类库,可以通过简单的注解来简化和消除一些必须有但显得很臃肿的Java代码。
通过注解的形式自动生成构造器、getter/setter、equals、hashcode、toString等方法,并可以自动化生成日志变量,简化java开发、提高效率。
注解 作用
@Getter/@Setter
为所有的属性提供get/set方法
@ToString
会给类自动生成易阅读的 toString 方法
@EqualsAndHashCode
根据类所拥有的非静态字段自动重写 equals 方法和 hashCode 方法
@Data
提供了更综合的生成代码功能(@Getter + @Setter + @ToString + @EqualsAndHashCode)
@NoArgsConstructor
为实体类生成无参的构造器方法
@AllArgsConstructor
为实体类生成除了static修饰的字段之外带有各参数的构造器方法。
使用
引入依赖1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.projectlombok</groupId > <artifactId > lombok</artifactId > </dependency >
在实体类加入注解1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 import lombok.Data;@Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class User { private Integer id; private String name; private Short age; private Short gender; private String phone; }
Lombok的注意事项:
Lombok会在编译时,会自动生成对应的java代码
在使用lombok时,还需要安装一个lombok的插件(新版本的IDEA中自带)
正式进入Mybatis 参数占位符 在Mybatis中提供的参数占位符有两种:${...} 、#{...}
#{...}
执行SQL时,会将#{…}替换为?,生成预编译SQL,会自动设置参数值
使用时机:参数传递,都使用#{…}
${...}
拼接SQL。直接将参数拼接在SQL语句中,存在SQL注入问题
使用时机:如果对表名、列表进行动态设置时使用
注意事项:在项目开发中,建议使用#{…},生成预编译SQL,防止SQL注入安全。
CURD 删除 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Mapper public interface EmpMapper { @Delete("delete from emp where id = #{id}") public void delete (Integer id) ; }
新增 基本新增——
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Mapper public interface EmpMapper { @Insert("insert into emp(username, name, gender, image, job, entrydate, dept_id, create_time, update_time) values (#{username}, #{name}, #{gender}, #{image}, #{job}, #{entrydate}, #{deptId}, #{createTime}, #{updateTime})") public void insert (Emp emp) ; }
主键返回——
例子:在数据添加成功后,需要获取插入数据库数据的主键。比如在学生完成夏令营报名后,需要获取报名号ID,以发送给学生。
默认情况下,执行插入操作时,是不会主键值返回的。如果我们想要拿到主键值,需要在Mapper接口中的方法上添加一个Options注解,并在注解中指定属性useGeneratedKeys=true和keyProperty=”实体类属性名”
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Mapper public interface EmpMapper { @Options(useGeneratedKeys = true,keyProperty = "id") @Insert("insert into emp(username, name, gender, image, job, entrydate, dept_id, create_time, update_time) values (#{username}, #{name}, #{gender}, #{image}, #{job}, #{entrydate}, #{deptId}, #{createTime}, #{updateTime})") public void insert (Emp emp) ; }
更新 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Mapper public interface EmpMapper { @Update("update emp set username=#{username}, name=#{name}, gender=#{gender}, image=#{image}, job=#{job}, entrydate=#{entrydate}, dept_id=#{deptId}, update_time=#{updateTime} where id=#{id}") public void update (Emp emp) ; }
查询 主键查询 根据Id查询该员工信息
1 2 3 4 5 @Mapper public interface EmpMapper { @Select("select id, username, password, name, gender, image, job, entrydate, dept_id, create_time, update_time from emp where id=#{id}") public Emp getById (Integer id) ; }
数据封装
我们看到查询返回的结果中大部分字段是有值的,但是deptId,createTime,updateTime这几个字段是没有值的 ,而数据库中是有对应的字段值的
【原因如下】
实体类属性名和数据库表查询返回的字段名一致,mybatis会自动封装。
如果实体类属性名和数据库表查询返回的字段名不一致,不能自动封装 。
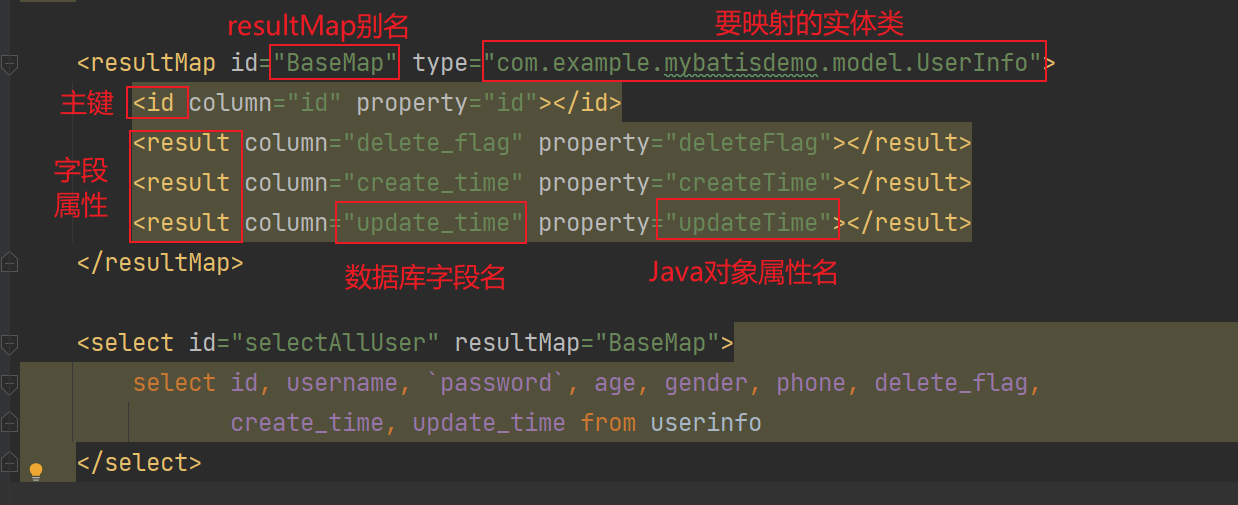
【解决方案】起别名 :在SQL语句中,对不一样的列名起别名,别名和实体类属性名一样手动结果映射 :通过 @Results及@Result 进行手动结果映射
1 2 3 4 5 @Results({@Result(column = "dept_id", property = "deptId"), @Result(column = "create_time", property = "createTime"), @Result(column = "update_time", property = "updateTime")}) @Select("select id, username, password, name, gender, image, job, entrydate, dept_id, create_time, update_time from emp where id=#{id}") public Emp getById (Integer id) ;
开启驼峰命名(推荐) :如果字段名与属性名符合驼峰命名规则,mybatis会自动通过驼峰命名规则映射
驼峰命名规则: abc_xyz => abcXyz
表 中字段名:abc_xyz
类 中属性名:abcXyz
1 2 mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case =true
要使用驼峰命名前提是 实体类的属性 与 数据库表中的字段名严格遵守驼峰命名。
条件查询 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Mapper public interface EmpMapper { @Select("select * from emp " + "where name like '%${name}%' " + "and gender = #{gender} " + "and entrydate between #{begin} and #{end} " + "order by update_time desc") public List<Emp> list (String name, Short gender, LocalDate begin, LocalDate end) ; }
上述方案容易有sql注入的风险,可以使用MySQL提供的字符串拼接函数:concat('%' , '关键字' , '%')
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Mapper public interface EmpMapper { @Select("select * from emp " + "where name like concat('%',#{name},'%') " + "and gender = #{gender} " + "and entrydate between #{begin} and #{end} " + "order by update_time desc") public List<Emp> list (String name, Short gender, LocalDate begin, LocalDate end) ; }
XML与SQL 使用Mybatis的注解方式,主要是来完成一些简单的增删改查功能。如果需要实现复杂的SQL功能,建议使用XML来配置映射语句,也就是将SQL语句写在XML配置文件中。
在Mybatis中使用XML映射文件方式开发,需要符合一定的规范:
XML映射文件的名称与Mapper接口名称一致,并且将XML映射文件和Mapper接口放置在相同包下 (同包同名)
XML映射文件的namespace属性为Mapper接口全限定名一致
XML映射文件中sql语句的id与Mapper接口中的方法名一致,并保持返回类型一致。
xml映射文件中的dtd约束,直接从mybatis官网复制即可——
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" > <mapper namespace ="" > </mapper >
使用Mybatis的注解,主要是来完成一些简单的增删改查功能。如果需要实现复杂的SQL功能,建议使用XML来配置映射语句。
映射配置 解决名字不一样的问题
1 2 3 4 5 <select id ="selectUser" resultType ="user" > select * from user </select >
实际操作 增加
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <insert id ="insertUser" > insert into userinfo (username, password, age, gender, phone) values (#{username}, #{password}, #{age},#{gender},#{phone}) </insert > <insert id ="insertUser" useGeneratedKeys ="true" keyProperty ="id" > insert into userinfo (username, password, age, gender, phone) values (#{username}, #{password}, #{age},#{gender},#{phone}) </insert >
删除 1 2 3 <delete id ="deleteUser" > delete from userinfo where id = #{id} </delete >
若数据库的字段名和springboot的entity字段名不一致,可以用如下方法
1 2 3 4 @Mapper public interface UserMapper { @Delete("DELETE FROM userinfo WHERE id = #{pojoID}") int deleteUser (@Param("pojoID") Long pojoID) ;
1 2 3 4 <delete id ="deleteUser" > DELETE FROM userinfo WHERE id = #{pojoID} </delete >
更新
1 2 3 <update id="updateUser" > update userinfo set username=#{username} where id=#{id} </update>
动态SQL 若条件是动态的,是可以不传递的,也可以只传递其中的1个或者2个或者全部。
正确做法是:传递了参数,再组装这个查询条件;如果没有传递参数,就不应该组装这个查询条件。SQL语句会随着用户的输入或外部条件的变化而变化,我们称为:动态SQL 。
IF <if>:用于判断条件是否成立。使用test属性进行条件判断,如果条件为true,则拼接SQL。1 2 3 <if test ="条件表达式" > 要拼接的sql语句 </if >
举例——
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <select id ="list" resultType ="com.itheima.pojo.Emp" > select * from emp where <if test ="name != null" > name like concat('%',#{name},'%') </if > <if test ="gender != null" > and gender = #{gender} </if > <if test ="begin != null and end != null" > and entrydate between #{begin} and #{end} </if > order by update_time desc </select >
WHERE 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <select id ="list" resultType ="com.itheima.pojo.Emp" > select * from emp <where > <if test ="name != null" > and name like concat('%',#{name},'%') </if > <if test ="gender != null" > and gender = #{gender} </if > <if test ="begin != null and end != null" > and entrydate between #{begin} and #{end} </if > </where > order by update_time desc </select >
如果where中的if都是空的,那么 SQL 语句将不包含 WHERE 子句,MyBatis 将使用参数的非空性来智能地构建查询,这样可以避免产生无效的 SQL 语句,减少不必要的性能开销。
SET 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" > <mapper namespace ="com.itheima.mapper.EmpMapper" > <update id ="update" > update emp set <if test ="username != null" > username=#{username}, </if > <if test ="name != null" > name=#{name}, </if > <if test ="gender != null" > gender=#{gender}, </if > <if test ="image != null" > image=#{image}, </if > <if test ="job != null" > job=#{job}, </if > <if test ="entrydate != null" > entrydate=#{entrydate}, </if > <if test ="deptId != null" > dept_id=#{deptId}, </if > <if test ="updateTime != null" > update_time=#{updateTime} </if > where id=#{id} </update > </mapper >
使用set标签,代替update语句中的set关键字 ,并会删掉额外的逗号
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" > <mapper namespace ="com.itheima.mapper.EmpMapper" > <update id ="update" > update emp <set > <if test ="username != null" > username=#{username}, </if > <if test ="name != null" > name=#{name}, </if > <if test ="gender != null" > gender=#{gender}, </if > <if test ="image != null" > image=#{image}, </if > <if test ="job != null" > job=#{job}, </if > <if test ="entrydate != null" > entrydate=#{entrydate}, </if > <if test ="deptId != null" > dept_id=#{deptId}, </if > <if test ="updateTime != null" > update_time=#{updateTime} </if > </set > where id=#{id} </update > </mapper >
FOREACH title:foreach的基本用法 1 2 3 <foreach collection ="集合名称" item ="集合遍历出来的元素/项" separator ="每一次遍历使用的分隔符" open ="遍历开始前拼接的片段" close ="遍历结束后拼接的片段" > </foreach >
举例——
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" > <mapper namespace ="com.itheima.mapper.EmpMapper" > <delete id ="deleteByIds" > delete from emp where id in <foreach collection ="ids" item ="id" separator ="," open ="(" close =")" > #{id} </foreach > </delete > </mapper >
若传入1,2,3。那么生成的sql语句将会是delete from emp where id in (1,2,3);
INCLUDE 这个标签就是类似于cpp的#include,把库函数纳入起来。
这里就是把重复的预定义的sql纳入进来。
首先抽取重复代码1 2 3 <sql id ="commonSelect" > select id, username, password, name, gender, image, job, entrydate, dept_id, create_time, update_time from emp </sql >
然后,就可以直接引用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 <select id ="list" resultType ="com.itheima.pojo.Emp" > <include refid ="commonSelect" /> <where > <if test ="name != null" > name like concat('%',#{name},'%') </if > <if test ="gender != null" > and gender = #{gender} </if > <if test ="begin != null and end != null" > and entrydate between #{begin} and #{end} </if > </where > order by update_time desc </select >
MyBatis-PLUS 官方文档
准备依赖 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <dependency > <groupId > mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-java</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.projectlombok</groupId > <artifactId > lombok</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.baomidou</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 3.0.5</version > </dependency >
说明:使用 mybatis-plus 可以帮助我们节省大量的代码,尽量不要同时导入 mybatis 和 mybatis-plus!
配置扫描所有mapper,使用MapperScan
hl:MapperScan 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @SpringBootApplication @MapperScan("com.baomidou.mybatisplus.samples.quickstart.mapper") public class Application { public static void main (String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); } }
实体与映射 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @TableName(value = "user") public class User implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L ; @TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO) private Integer id; private String name; private String password; private String username; }
CRUD Mapper interface mapper改造:继承BaseMapper接口
1 2 3 public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper <User> { }
Insert 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 int insert (T entity) ;User user = new User ();user.setName("John Doe" ); user.setEmail("john.doe@example.com" ); int rows = userMapper.insert(user); if (rows > 0 ) { System.out.println("User inserted successfully." ); } else { System.out.println("Failed to insert user." ); }
delete 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 int delete (@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> wrapper) ;QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper <>(); queryWrapper.gt("age" , 25 ); int rows = userMapper.delete(queryWrapper); if (rows > 0 ) { System.out.println("Users deleted successfully." ); } else { System.out.println("No users deleted." ); } int deleteBatchIds (@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection<? extends Serializable> idList) ;List<Integer> ids = Arrays.asList(1 , 2 , 3 ); int rows = userMapper.deleteBatchIds(ids); if (rows > 0 ) { System.out.println("Users deleted successfully." ); } else { System.out.println("No users deleted." ); } int deleteById (Serializable id) ;int deleteByMap (@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map<String, Object> columnMap) ;Map<String, Object> columnMap = new HashMap <>(); columnMap.put("age" , 30 ); int rows = userMapper.deleteByMap(columnMap); if (rows > 0 ) { System.out.println("Users deleted successfully." ); } else { System.out.println("No users deleted." ); }
Update 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 int update (@Param(Constants.ENTITY) T updateEntity, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> whereWrapper) ;UpdateWrapper<User> updateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper <>(); updateWrapper.gt("age" , 25 ); User updateUser = new User ();updateUser.setEmail("new.email@example.com" ); int rows = userMapper.update(updateUser, updateWrapper); if (rows > 0 ) { System.out.println("Users updated successfully." ); } else { System.out.println("No users updated." ); } int updateById (@Param(Constants.ENTITY) T entity) ;
select 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 T selectById (Serializable id) ; T selectOne (@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) ; List<T> selectBatchIds (@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection<? extends Serializable> idList) ; List<T> selectList (@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) ; List<T> selectByMap (@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map<String, Object> columnMap) ; List<Map<String, Object>> selectMaps (@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) ; QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper <>(); queryWrapper.gt("age" , 25 ); List<Map<String, Object>> userMaps = userMapper.selectMaps(queryWrapper); for (Map<String, Object> userMap : userMaps) { System.out.println("User Map: " + userMap); } List<Object> selectObjs (@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) ; IPage<T> selectPage (IPage<T> page, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) ; IPage<User> page = new Page <>(1 , 10 ); QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper <>(); queryWrapper.gt("age" , 25 ); IPage<User> userPage = userMapper.selectPage(page, queryWrapper); List<User> userList = userPage.getRecords(); long total = userPage.getTotal();System.out.println("Total users (age > 25): " + total); for (User user : userList) { System.out.println("User: " + user); } IPage<Map<String, Object>> selectMapsPage (IPage<T> page, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) ; Integer selectCount (@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) ;
Service interface 在 Service 层提供通用的数据库操作方法。你可以在 Service 层的任何地方使用它
save 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 boolean save (T entity) ;boolean saveBatch (Collection<T> entityList) ;boolean saveBatch (Collection<T> entityList, int batchSize) ;boolean saveOrUpdate (T entity) ;boolean saveOrUpdate (T entity, Wrapper<T> updateWrapper) ;boolean saveOrUpdateBatch (Collection<T> entityList) ;boolean saveOrUpdateBatch (Collection<T> entityList, int batchSize) ;
remove 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 boolean remove (Wrapper<T> queryWrapper) ;boolean removeById (Serializable id) ;boolean removeByMap (Map<String, Object> columnMap) ;boolean removeByIds (Collection<? extends Serializable> idList) ;